반응형
1. DarkNet

DarkNet은 YOLOv1이 feature map을 생성하기 위해 만들어진 독자적인 CNN이다.
## model.py
"""
Implementation of Yolo (v1) architecture
with slight modification with added BatchNorm.
"""
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
"""
Information about architecture config:
Tuple is structured by (kernel_size, filters, stride, padding)
"M" is simply maxpooling with stride 2x2 and kernel 2x2
List is structured by tuples and lastly int with number of repeats
"""
architecture_config = [
(7, 64, 2, 3),
"M",
(3, 192, 1, 1),
"M",
(1, 128, 1, 0),
(3, 256, 1, 1),
(1, 256, 1, 0),
(3, 512, 1, 1),
"M",
[(1, 256, 1, 0), (3, 512, 1, 1), 4],
(1, 512, 1, 0),
(3, 1024, 1, 1),
"M",
[(1, 512, 1, 0), (3, 1024, 1, 1), 2],
(3, 1024, 1, 1),
(3, 1024, 2, 1),
(3, 1024, 1, 1),
(3, 1024, 1, 1),
]
class CNNBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, **kwargs):
super(CNNBlock, self).__init__()
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, bias=False, **kwargs)
self.batchnorm = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
self.leakyrelu = nn.LeakyReLU(0.1)
def forward(self, x):
return self.leakyrelu(self.batchnorm(self.conv(x)))
class Yolov1(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels=3, **kwargs):
super(Yolov1, self).__init__()
self.architecture = architecture_config
self.in_channels = in_channels
self.darknet = self._create_conv_layers(self.architecture)
self.fcs = self._create_fcs(**kwargs)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.darknet(x)
return self.fcs(torch.flatten(x, start_dim=1))
def _create_conv_layers(self, architecture):
layers = []
in_channels = self.in_channels
for x in architecture:
if type(x) == tuple:
layers += [
CNNBlock(
in_channels, x[1], kernel_size=x[0], stride=x[2], padding=x[3],
)
]
in_channels = x[1]
elif type(x) == str:
layers += [nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=(2, 2), stride=(2, 2))]
elif type(x) == list:
conv1 = x[0]
conv2 = x[1]
num_repeats = x[2]
for _ in range(num_repeats):
layers += [
CNNBlock(
in_channels,
conv1[1],
kernel_size=conv1[0],
stride=conv1[2],
padding=conv1[3],
)
]
layers += [
CNNBlock(
conv1[1],
conv2[1],
kernel_size=conv2[0],
stride=conv2[2],
padding=conv2[3],
)
]
in_channels = conv2[1]
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
def _create_fcs(self, split_size, num_boxes, num_classes):
S, B, C = split_size, num_boxes, num_classes
# In original paper this should be
# nn.Linear(1024*S*S, 4096),
# nn.LeakyReLU(0.1),
# nn.Linear(4096, S*S*(B*5+C))
return nn.Sequential(
nn.Flatten(),
nn.Linear(1024 * S * S, 496),
nn.Dropout(0.0),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.1),
nn.Linear(496, S * S * (C + B * 5)),
)
- config는 설명처럼 (kernel_size, filters, stride, padding)을 의미하고, "M"이면 Maxpooling(stride2, kernel2)이 수행된다.
- config의 [(), n]의 형태는 ()의 cfg가 n번 반복된다.(그림 상 3, 4번째 연산에 해당)
- _create_conv_layers 함수를 통해 CNN 구조를 만든다.
- DarkNet 뒷단의 fclayer를 만들기 위한 함수 _create_fcs 함수를 사용하는데, 여기 입력되는 kwargs는 기본적으로 split_size=7, num_boxes=2, num_classes=20이다. 이 kwargs에 따라 FC layer의 input과 output size를 계산하기 때문에 입력된다.
2. Loss

loss 계산에 필요한 하이퍼파라미터는 위 DarkNet의 fc layer에 입력된 split_size=7, num_boxes=2, num_classes=20가 필요하고, 추가적으로 noobj, coord를 지정해주어야 한다.
## loss.py
"""
Implementation of Yolo Loss Function from the original yolo paper
"""
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from utils import intersection_over_union
class YoloLoss(nn.Module):
"""
Calculate the loss for yolo (v1) model
"""
def __init__(self, S=7, B=2, C=20):
super(YoloLoss, self).__init__()
self.mse = nn.MSELoss(reduction="sum")
"""
S is split size of image (in paper 7),
B is number of boxes (in paper 2),
C is number of classes (in paper and VOC dataset is 20),
"""
self.S = S
self.B = B
self.C = C
# These are from Yolo paper, signifying how much we should
# pay loss for no object (noobj) and the box coordinates (coord)
self.lambda_noobj = 0.5
self.lambda_coord = 5
def forward(self, predictions, target):
# predictions are shaped (BATCH_SIZE, S*S(C+B*5) when inputted
predictions = predictions.reshape(-1, self.S, self.S, self.C + self.B * 5)
# Calculate IoU for the two predicted bounding boxes with target bbox
iou_b1 = intersection_over_union(predictions[..., 21:25], target[..., 21:25])
iou_b2 = intersection_over_union(predictions[..., 26:30], target[..., 21:25])
ious = torch.cat([iou_b1.unsqueeze(0), iou_b2.unsqueeze(0)], dim=0)
# Take the box with highest IoU out of the two prediction
# Note that bestbox will be indices of 0, 1 for which bbox was best
iou_maxes, bestbox = torch.max(ious, dim=0)
exists_box = target[..., 20].unsqueeze(3) # in paper this is Iobj_i
# ======================== #
# FOR BOX COORDINATES #
# ======================== #
# Set boxes with no object in them to 0. We only take out one of the two
# predictions, which is the one with highest Iou calculated previously.
box_predictions = exists_box * (
(
bestbox * predictions[..., 26:30]
+ (1 - bestbox) * predictions[..., 21:25]
)
)
box_targets = exists_box * target[..., 21:25]
# Take sqrt of width, height of boxes to ensure that
box_predictions[..., 2:4] = torch.sign(box_predictions[..., 2:4]) * torch.sqrt(
torch.abs(box_predictions[..., 2:4] + 1e-6)
)
box_targets[..., 2:4] = torch.sqrt(box_targets[..., 2:4])
box_loss = self.mse(
torch.flatten(box_predictions, end_dim=-2),
torch.flatten(box_targets, end_dim=-2),
)
# ==================== #
# FOR OBJECT LOSS #
# ==================== #
# pred_box is the confidence score for the bbox with highest IoU
pred_box = (
bestbox * predictions[..., 25:26] + (1 - bestbox) * predictions[..., 20:21]
)
object_loss = self.mse(
torch.flatten(exists_box * pred_box),
torch.flatten(exists_box * target[..., 20:21]),
)
# ======================= #
# FOR NO OBJECT LOSS #
# ======================= #
#max_no_obj = torch.max(predictions[..., 20:21], predictions[..., 25:26])
#no_object_loss = self.mse(
# torch.flatten((1 - exists_box) * max_no_obj, start_dim=1),
# torch.flatten((1 - exists_box) * target[..., 20:21], start_dim=1),
#)
no_object_loss = self.mse(
torch.flatten((1 - exists_box) * predictions[..., 20:21], start_dim=1),
torch.flatten((1 - exists_box) * target[..., 20:21], start_dim=1),
)
no_object_loss += self.mse(
torch.flatten((1 - exists_box) * predictions[..., 25:26], start_dim=1),
torch.flatten((1 - exists_box) * target[..., 20:21], start_dim=1)
)
# ================== #
# FOR CLASS LOSS #
# ================== #
class_loss = self.mse(
torch.flatten(exists_box * predictions[..., :20], end_dim=-2,),
torch.flatten(exists_box * target[..., :20], end_dim=-2,),
)
loss = (
self.lambda_coord * box_loss # first two rows in paper
+ object_loss # third row in paper
+ self.lambda_noobj * no_object_loss # forth row
+ class_loss # fifth row
)
return loss
2.1. localization loss
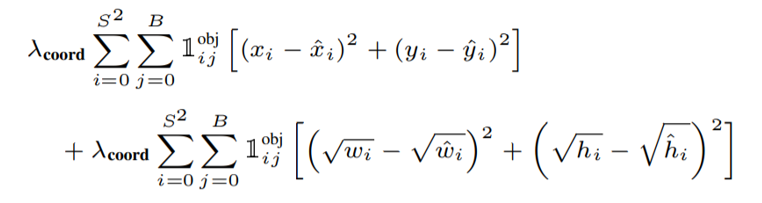
predictions이 입력되었을 때, 이를 (batch, 7, 7, 30)사이즈로 resize 시켜주고, num_boxes가 2개이므로 아래 box 좌표에 해당하는 값을 target과의 IoU를 계산하고, 두 tensor를 concat한다. 여기서 best box에 target과의 IoU값이 더 큰 box의 인덱스가 저장된다.
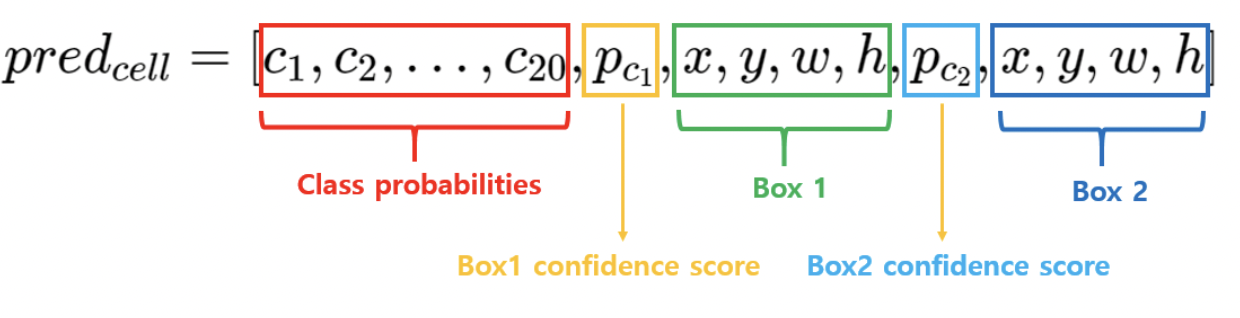
- exist_box는 target[..., 3]의 값으로 gt가 존재한다면 1, 존재하지 않으면 0이 된다.
- 코드에서 bestbox값을 활용해 predicted box 좌표를 구하는데, 이 코드는 num_boxs가 2인 경우(논문 설정)에만 적용할 수 있는 코드인 것 같다.
- 이 후 prediction과 target 둘 다 w, h에 해당하는 좌표에 루트를 씌어준다
- Localizatoin loss의 수식을 처음 보면 뭔가 싶었는데, 결국 w, h에는 루트를 씌운 x, y, w, h에 대한 mse이다.
- 수식의 labmda_coord 가중치는 전체 로스 합산 시 적용된다.
2.2 Confidence loss
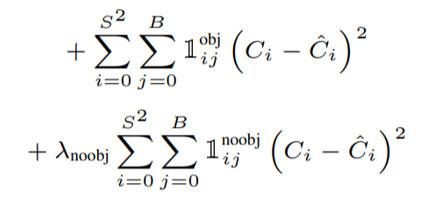
- 코드에서 수식의 첫 번째 항인 object가 존재하는 경우의 Loss를 먼저 구해준다. 여기서도 best box의 인덱스값을 활용하는데, loss를 구하기 전부터 class prob + bestbox(confidence score, x, y, w, h)를 구해놓고 시작하는게 더 낫지 않나 싶다.
- 위에서처럼 방금 best box의 값을 미리 구해놓고 시작하면 되지 않을까 생각했는데, no_object_loss를 두 번 구하는 과정에서 왜 코드를 이렇게 작성했는지 이해되었다. 해당 grid cell의 두 bbox가 전부 배경으로 판정(exists_box=0)되었을 때, 두 bbox에 대한 no_object_loss를 전부 구해주어야 한다.
- 여기서 object_loss와 no_object_loss를 합산하지 않은 이유는 뒤에 no_object_loss에 대한 가중치 lambda를 따로 적용시키기 위해서다.
2.3 Classification loss
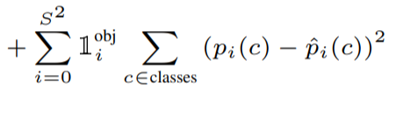
Classification loss는 predictions[..., :20]에 해당하며 이는 20개 class에 대한 prob을 나타낸다. 이와 target과의 mse loss를 계산한다.
이 후 세 Loss에 대한 가중치를 적용시키고 합산한다.
반응형
'DL > Code' 카테고리의 다른 글
| YOLOv3 Pytorch 코드 리뷰 (0) | 2024.01.26 |
|---|---|
| MDGAN : Mask guided Generation Method for Industrial Defect Images with Non-uniform Structures 코드 구현 및 리뷰 (1) | 2024.01.24 |
| Transformer Pytorch 코드 리뷰 (1) | 2024.01.24 |


